15d. Transhumeral Harnessing Variations
Transhumeral harnesses are individually designed to maximize the efficiency of the control system, the suspension of the prosthesis and ideally fit comfortably on the person. Variations on harness designs may include any of the elements from the following: Hessing pad, Shoulder Saddle and Chest Strap, Triple Control Harness, Bilateral harness and Shoulder Disarticulation Harness designs.
In addition, material selection is important. Most harnesses are fabricated with polypropylene webbing, but other options like climbing webbing may be used if increased tension strength is necessary. Finally, buckles might be used to ease one-handed application/removal such as fidlock, click medical or others, e.g., WBC Industries. Be creative in your design. During your fitting appointment, consider these questions:
- How does the location and path of the control attachment strap affect the efficiency of force and excursion?
- How does the force on the strap and thus the cable affect the socket fit on the residual limb?
- How do the suspension straps resist gravity and the weight of the prosthesis throughout shoulder ROM?
- How to improve comfort?
Ultimately, the key points on harnessing must be adhered to:
- The harness suspends the prosthesis by distributing the load and maintains prosthetic stability through various ROM;
- The control system allows for the transmission of power from the individuals body motion to the prosthesis;
- Harness and cable system together should be operable with relatively inconspicuous body motions.
- The harness must be easy for the person to don, doff, launder; and
- It must be comfortable and durable.
Variations[1]
- Hessing Pap
- Shoulder Saddle and Chest Strap
- Triple Control Harness
- Bilateral Transhumeral Harness
| Hessing Pad
Purpose: to distribute and offload weight/pressure from the contralateral axilla Located laterally on chest wall under the scapula from about T7-T11 ribs. Notice that it does not extend very far medially. Materials: Leather, Plastic, Spenco Reference: Fillauer
|
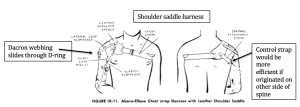
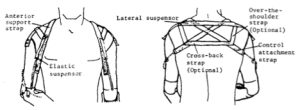
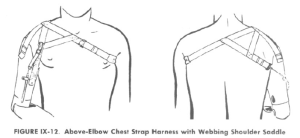
| Shoulder Saddle and Chest Strap
The greatest disadvantages of the chest strap harness are difficulty in applying and removing, and a tendency to rotate about the chest because of lack of a stable anchoring point. In addition, many amputees, particularly women, cannot tolerate the chest strap. In general, the use of the chest strap harness is confined to those patients who must lift heavy loads, or who cannot tolerate the axilla loop, even with a pad, or who have habitually worn the chest strap harness and do not wish to change. (NYU 1979). The control attachment strap is usually connected to the lateral corner of the posterior portion of the shoulder saddle.
|
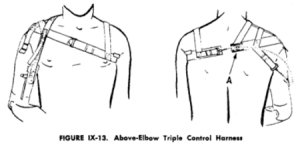
| Triple Control Harness
Scapular abduction is used with the triple control system, to operate the TD through a Bowden cable control. Arm flexion is used only to flex the forearm. Each function is separately harnessed and considerable skill is required to manage the operations independently. The separation is accomplished by slitting the harness in back, attaching the cable to one side of it, and the cable housing to the other. When the patient abducts the scapulae, the two halves of the harness are pulled apart at the break, thus pulling on the cable and operating the TD.[2] The NYU Triple Control Harness consists of 3 control elements:
Consider challenges with separation of control for the patient.
|
| Bilateral Transhumeral Harness
The bilateral harness is a combination of two above-elbow Figure-8 harnesses; each axilla loop is replaced by an attachment to the opposite prosthesis. A cross-back strap and two over-the-shoulder straps may be added to improve harness stability. The dual control system used on each prosthesis is identical with that used on a unilateral above-elbow prosthesis.
The fairlead control cable system is used in the above-elbow prosthesis to transmit force for two functions: elbow flexion and terminal device operation. A second cable controls elbow locking and unlocking: the elbow-lock cable. When the elbow is extended and unlocked, flexing the shoulder transmits force to the forearm lever loop, raising the forearm to the desired level. If the user wishes to use the TD at this point, he/she locks the elbow and then operates the TD by continuation of the control motion, i.e. shoulder flexion.
Control motions:
|

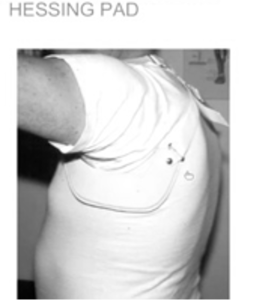 The Hessing pad can replace axilla loop: Fits under scapula on contralateral axilla
The Hessing pad can replace axilla loop: Fits under scapula on contralateral axilla