Additive Manufacturing (3-D Printing)
Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, is a process where three-dimensional objects are built layer by layer from a digital design.
- Capture Impression
- CAD (Computer Aided Design) Software – Parametric modeling
- Photogrammetry: Multiple digital photos used to reconstruct 3D object, e.g., 123D catch
- Optical 3D Scan (P&O commonly uses this)
- Shape data converted to electronic file for modification and printing
- Structured Light – Poor reliability; High precision when conditions are stable
- Laser Triangulation – Good reliability; Highest consistency of the three technologies
- LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) – Excellent reliability; Good consistency but can vary with range and surface properties
-
Surface preparation for scanning
- Cover residual limb with stockinette
- Use targeting stickers or markers
- Apply temporary reflective spray or powder on components
- Modify Design
- Parametric modelling E.g., components like feet, elbows, hinges, tooling, dummies
- Nonparametric modelling E.g., the part that fits against the body, like the socket, orthosis
- Can begin with a scan, 3-d objects that are then sculpted
- Common CAD Terms
-
Mesh: Collection of stitched surface patches to represent 3D data model. A way to represent solid objects through polygon division. E.g., Triangle meshes, quad meshes, and n-gon meshes are all types of polygon 3D meshes
-
Spline: A curve that uses a series of control points and other mathematical principles to define the location and form of the curve. Defines precise curved movements of the printer.
-
-
Manifold errors refer to issues with the geometry that prevent the model from being printable. These errors include holes, gaps, intersecting triangles, and flipped normals. These errors can cause the 3D printing software to misinterpret the instructions, leading to printing failures or defects.
- Guidelines to reduct errors: The CAD model must:
- Have sufficient wall thickness (consistent with the material used)
- Have support for overhangs
- Prevent manifold errors:
- Closed mesh (no open edges, holes, gaps, or faces), i.e., watertight
- Not have internal geometry
- Edges mush not be shared by more than 2 faces (non-manifold edges)
- Fit within the printer’s limits (i.e., dimensions)
- Fabricate
-
Computer aided manufacturing (CAM), the use of software and computer-controlled machinery to automate a manufacturing process. Three components are necessary for a CAM system to function:
-
Software that tells a machine how to make a product by generating toolpaths
-
Industrial machinery that can turn raw material into a finished product
-
Post-processing converts toolpaths into a language machines can understand (i.e., x, y, z coordinates)
-
- Subtractive manufacturing (Synonyms: Carving) involves material removal with turning, milling, drilling, grinding, cutting, and boring.
- Additive manufacturing: (Synonyms: 3D Printing, Rapid Manufacturing, Additive Manufacturing, Layer Manufacturing)—An automated method to build models, prototypes, tools and manufactured parts directly from CAD data, that constructs these parts by depositing and bonding materials on a layer-by-layer basis.
- CAD model is translated by “Slicer” software into individual layers (e.g., Slic3r)
- 3d Printing Technologies
-
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) Technology
-
Stereolithography (SLA) Technology
-
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) Technology
-
Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) Technology
-
PolyJet Technology
-
- Potential limitations: Interlayer adhesion (aka delamination)
- Material Selection
- Use the same factors as listed on the Thermoplastics page in this book to select the appropriate materials.
-
Examples
-
PLA: prototypes. It is inexpensive and compostable
-
ABS: LEGO bricks, small kitchen appliances, keyboard keycaps, automotive components, protective headgear and musical instruments.
-
HDPE: Food and beverage containers: Milk jugs, shampoo bottles, bleach bottles, detergent bottles, and yogurt tubs (high toughness)
- Nylon:
- PETG: Test sockets (poor toughness, low impact resistance)
-
- Links to manufacturers
- https://www.stratasys.com/en/materials/materials-catalog/?filter=MT_PolyJet+J5_MediJet+J850_Digital_Anatomy
- https://www.3dsystems.com/material-finder?printer-compatibility%5B0%5D=ProJet%20MJP%202500%2F2500%20Plus
- https://taulman3d.com/how-to-choose.html
- https://www.digitaltrends.com/cool-tech/abs-vs-pla-3d-printing-materials-comparison/
-
Additive Manufacturing – Key Takeaways
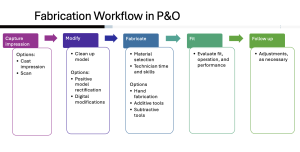
- Digital fabrication workflow in P&O includes capturing the impression, modifying the positive model, fabrication, evaluation of the device, and follow up to ensure quality.
- Digital models are created through photogammetry, optical 3D scanning, or CAD modeling.
- Ensure quality surface prep when using Structured light and LiDAR scanners: use stockinette covering, targeting stickers or markers, or reflective spray/powder on components, as needed.
- CAD modeling can be feature-based (building designs using parametric features and constraints) or direct modeling (modifying scanned or imported geometry directly); models are built either from patient measurements using CAD tools, or by modifying scanned limb geometry to create the final design.
- 3D printing builds structures layer-by-layer, making interlayer adhesion critical. Print orientation must account for this limitation.
- Digital models require “slicer” software to generate printable layers
- Material selection should consider strength, stiffness, and durability requirements.
A form of drafting in which parameters and constraints drive object size and location to produce drawings with features that adapt to changes made to other features.
Nonparametric modeling in 3D printing refers to a design approach where the geometry of a 3D model is created and manipulated without relying on predefined parameters or rules.
In 3D printing, a "manifold" or "watertight" model is one that is completely closed and has no holes or leaks, meaning it can be physically printed without issues. A manifold object has a clearly defined inside and outside, and every edge is connected to exactly two faces. Non-manifold models, on the other hand, have issues like holes, overlapping edges, or faces pointing in the wrong direction, which can cause printing problems.
