34 Rivets
PPE
- Use ear protection
- Use safety glasses
- Close toe shoes should be worn in all lab area

General Technique Tips
- Determine size and location of hole. The thru hole edge distance should be located at least two fastener diameters from an edge to prevent pull out failure.
- Drill hole. If drilling into metal, use a punch to create a small indent in the object to help direct the drill bit.
- Use the hammer, setter, and domer to round the head of the rivet.
- May use an anvil or a riveting bar to stabilize the rivet when hitting it.
- Place rivet through the hole and place the burr (if needed) on top of the rivet.
- Use burrs when riveting any non-metallic material, e.g., chafes, leather or plastic. The burr creates a larger surface area for the rivet to smash against.
- There is no need for burrs when riveting metal to metal
- If using a burr, use the hammer with the setter to push the burr next to the non-metallic material.
- Use the diagonal cutters to cut the copper rivet close to the surface of the rivet.
- Use the ball-peen hammer to roll the edges of the rivet, pulling the copper up
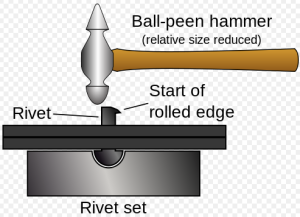 and over the surface of the burr to bind the pieces together. The tightness between the two materials (e.g., plastic) will increase when the rivet is rounded.
and over the surface of the burr to bind the pieces together. The tightness between the two materials (e.g., plastic) will increase when the rivet is rounded. - Now place the rounder on the top of the cut end of the rivet and form new head to secure the burr.
- Round all sharp edges that might scratch the skin.
Video: Setting Traditional Saddlers Pure Copper Rivets
- Note: the author of this video calls the burr a washer.
definition
metalworking tool consisting of a large block of metal with a flattened top surface, upon which another object is struck (or "worked").
