Course Design Standards
Category: Images & Multimedia
Content should be presented in multiple forms—text, images, media, and interactives—to support the various ways that learners perceive and comprehend information.
Standard B4: Interactives
Description
Interactives should be presented to supplement understanding. Interactives should not be the only method of providing essential information.
This standard is related to the universal design of learning (UDL) principle: Provide multiple means of representation. Providing information in different forms supports the various ways that learners comprehend information. Including interactives in courses can be effective for conveying concepts, but engaging with complex interactive content can be challenging for people with disabilities.
DEI Application
Authoring tools (software that course developers use to create interactives) do not always produce interactive content that is accessible to all learners. For example, an interactive might require interaction that a learner cannot physically perform or might be overwhelming for the learner. Essential information that is presented as text can be read by screen readers. Likewise, captions and audio descriptions can make video accessible to learners.
Example
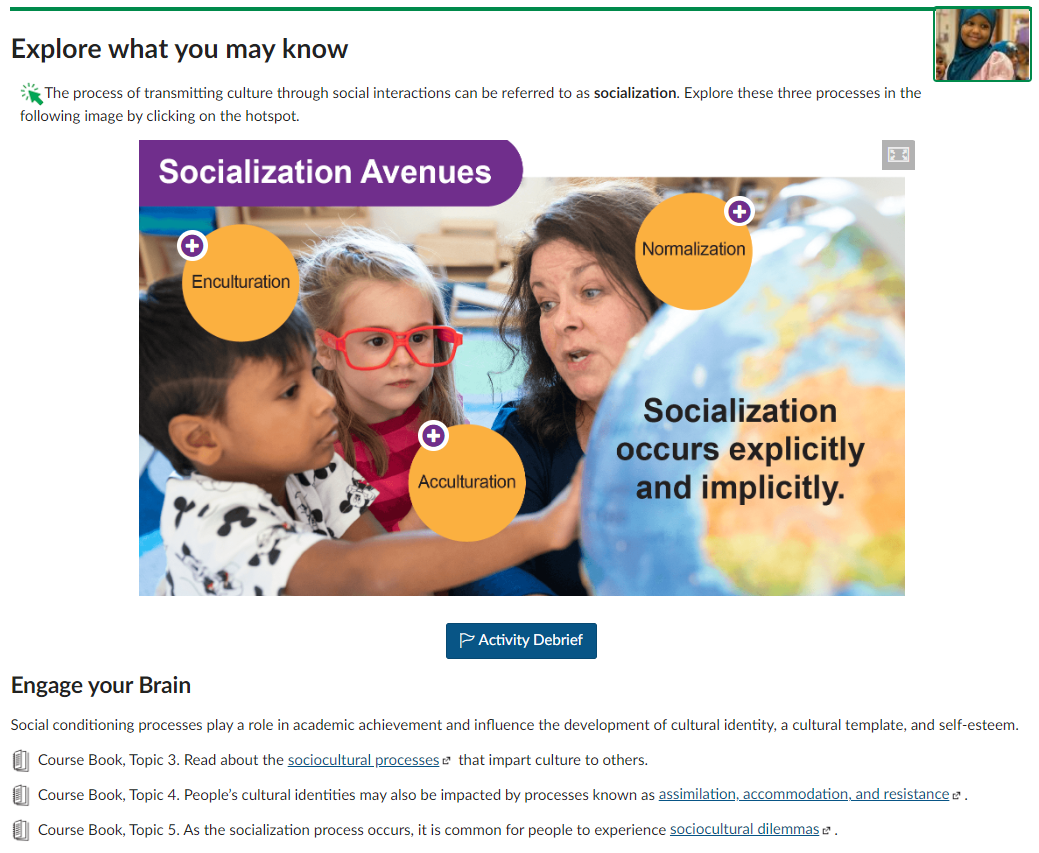
An example page from the Culturally Thriving and Socially Just Early Childhood Education course includes a “hotspot” interactive with the title “Socialization Avenues.” The interactive has a background image of a teacher and two children along with “hotspots” that learners can select to see brief descriptions of three socialization avenues: enculturation, normalization, and acculturation. On the same page, learners can access course books that have detailed text explanations and supporting images about enculturation, normalization, and acculturation.
Standard B5: Videos
Description
For video and audio recordings used in a course content, include the length, introductory text, and the speaker name when appropriate. A video (or audio recording) should not be the sole component on a course page.
DEI Application
Learners with limited time or limited internet access will appreciate knowing how long content will take to complete. Using introductory text provides context and can be used to introduce new terminology that will be present in the video or audio.
Example
Introductory text from Family Engagement Basics

Standard B6: Images with text
Description
Provide explanations for images with text or graphs. Explanations can be in the form of captions but preferably located in the text accompanying the image or graph. Decorative images do not need to be explained and should be have blank alt-text.
DEI Application
Learners using screen readers will be unable to read any text in an image and graphs. Neurodiverse learners and those unfamiliar with the graph axes will appreciate the explanation of the graph. When possible the explanation should be located close to the image or graph in keeping with the contiguity principle.
Example
Example graph with explanation from Child Development: Brain Building course book.

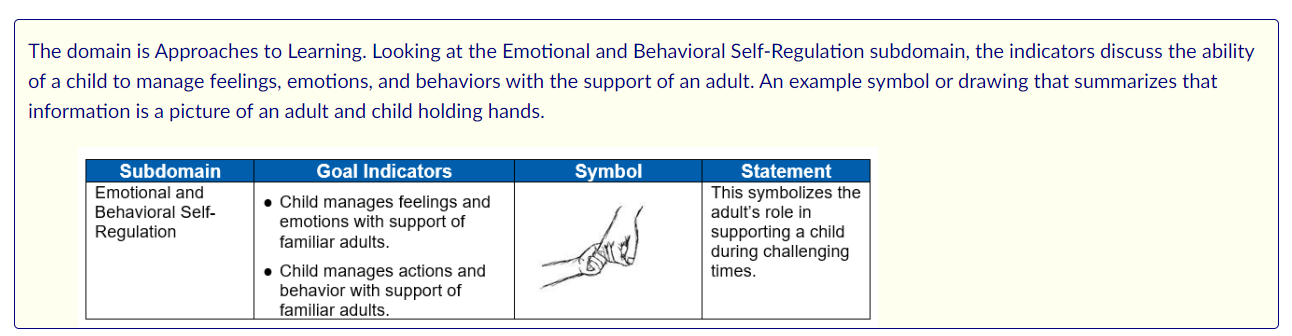
Standard B7: Tables
Description
Tables as images should be explained or reformatted as a true table with table caption, table headers, and scope. If the table is not used for direct use of tabular data, the table image should be used to minimize extraneous information.
DEI Application
When screen reader software encounters a table, the table headings and scope are announced to the user. If the learner does not need to interact directly with the table, using an image of the table is preferable.
Example
Table as image from Child Development: Brain Building