Course Design Standards
Category: Assessment
Assessment refers to the range graded activities that participants complete to demonstrate a functional understanding of concepts, topics, or skills.
Standard B10: Clear instructions
Description
The instructions and expectations are clear for activities, projects, discussions, and readings.
- Describe the purpose of an activity, project, discussion, or reading.
- Use a rubric to describe how the instructor (or peer) will assess an activity, project, discussion, or reading.
- Use ordered (numbered) lists to outline the steps needed to complete an activity, project, discussion, or reading.
- State the estimated time to complete an activity, project, discussion, or reading.
This standard is related to the Universal Design of Learning (UDL) guidelines: Provide options for Executive Functions.
DEI Application
Numbered and ordered lists help people who use screen readers. Neurodiverse learners benefit from clear instructions and structure. Estimated time would help learners with anxiety or time management issues.
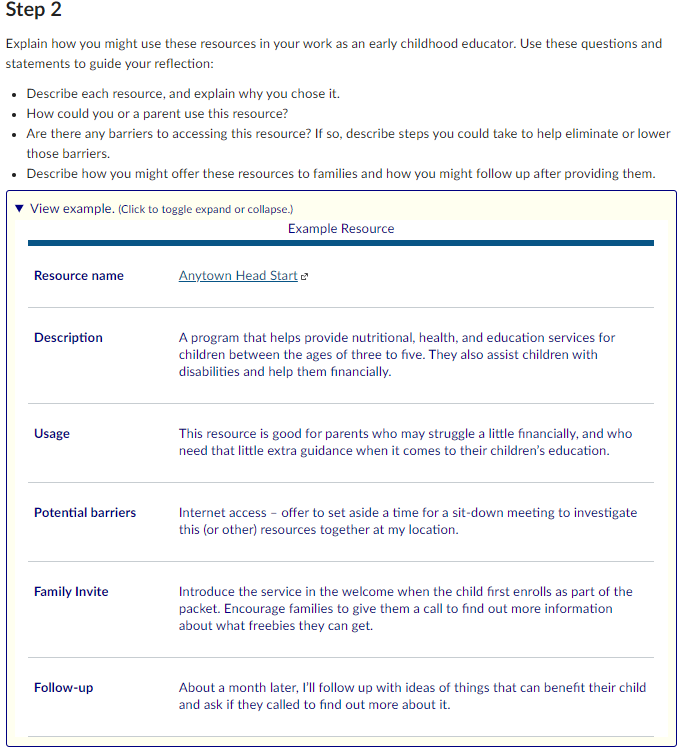
Example
Video assignment example with steps and time from Child Development Brain Building Session 4
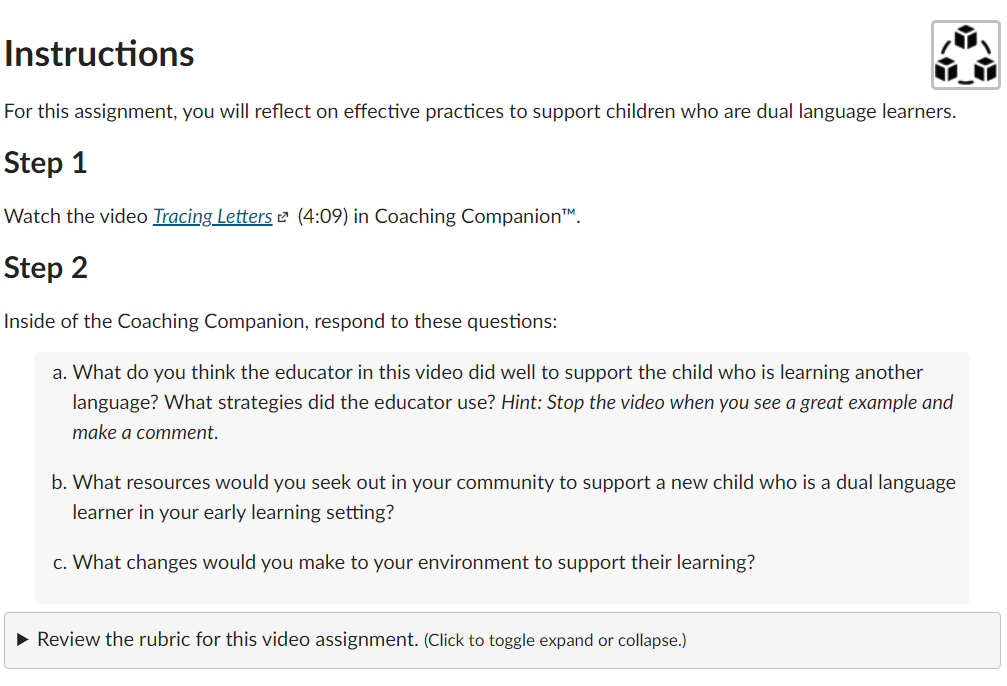
Standard B11: Variety of assignments
Description
There are multiple ways for participants to demonstrate what they have learned through the use of different types of test items, portfolios, presentations, and single-topic discussions. The assignments should not be all written text submissions, though the instructions may be text or text-equivalent for screen readers.
This standard is related to the UDL principle: Provide multiple means of Action & Expression. When possible, learners are given options for how to complete assignments that are not restricted to text-based responses. In addition, there may be different types of activities which include: quiz questions, discussions, videos, and other types of applied activities relevant to the early learning setting.
DEI Application
Including non-text-based assignment submissions will support learners who do not readily have access to word processing software or are otherwise unable to accurately complete a text-entry assignment: mobile users, dyslexic learners, and learners who struggle with written English.
Examples
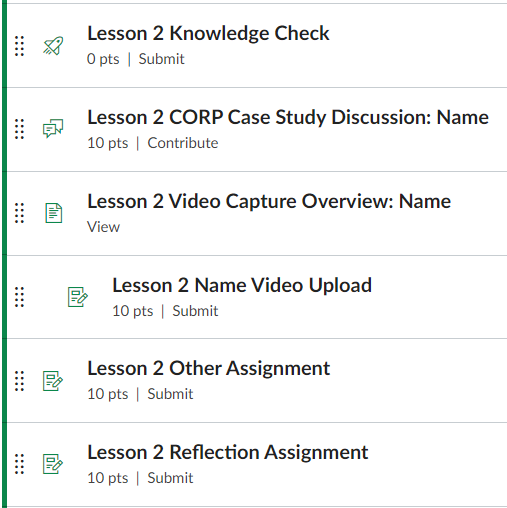
Different types of graded activities including quiz, discussion, video, other assignments, and reflection.
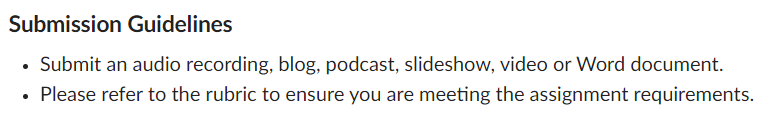
Submission guidelines from the weekly applied assignment:
LMS submission settings:

Standard B12: Unpublished alternate assignments
Description
For differentiated instruction, there are unpublished (visible only to instructors) alternate or optional assignments indicated in the Instructor Notes for that module or session. Our current recommendation is at least two alternate or optional assignments for 10 session courses and at least three alternate or optional assignments for 15 session courses.
DEI Application
Alternate assignments will enable instructors to differentiate instruction of upper and lower-level courses.
Examples
From Family Engagement Basics, Session 7 Instructor Notes

Unpublished assignment in Session 7
Standard B13: Major assignments and examples
Description
Break-up large or major assignments into smaller parts and distribute among course sessions. Major assignment pieces are distributed throughout the course.
For major (or complex) assignments, there are examples of alternative ways to complete the assignment. Examples should be available for online viewing (preferably from the course page) and not dependent on a download requiring specialized software (e.g., Word document, PowerPoint, and other MS Office applications).
DEI Application
Providing time management scaffolding for long-term assignments will alleviate learner anxiety about large multi-step assignments. Also, refrain from using the term “final assignment” to avoid confusion of being a last assignment or equivalent to a final examination.
Examples of alternative submissions will inspire all learners to engage with the material in ways that are naturally conducive to their learning. Mobile learners may encounter difficulties opening files requiring specialized software.
Examples
Achievement projects distributed among the course themes in Family Engagement Basics
Complex assignment with an example from Child Development: Brain Building.